Understanding Thoracic Spine Syndrome: A Comprehensive Guide
The thoracic spine syndrome is a complex condition that can drastically affect a person’s quality of life. Understanding this syndrome, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is paramount for both patients and practitioners in the health and medical field. With extensive insights into thoracic spine syndrome, we aim to enrich your knowledge, empowering you to make informed decisions regarding your health or the health of your patients.
What is Thoracic Spine Syndrome?
The thoracic spine, located in the upper and middle back, consists of 12 vertebrae (T1-T12) and serves several essential functions. These include protecting vital organs, facilitating movement, and providing structural support for the upper body. Thoracic spine syndrome refers to various pain syndromes that arise from this area, affecting the surrounding muscles, nerves, and ligaments. Understanding the complexities of this syndrome can help in the effective management of symptoms.
Types of Thoracic Spine Syndrome
Thoracic spine syndrome can manifest in several ways, each presenting unique challenges:
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: This occurs when blood vessels or nerves in the thoracic outlet (the area between your collarbone and first rib) become compressed.
- Thoracic Disc Herniation: This condition happens when the discs in the thoracic spine become damaged or degenerate, causing pain and discomfort.
- Myofascial Pain Syndrome: A chronic pain disorder that affects the connective tissue in the muscles, leading to pain and discomfort in the thoracic region.
Causes of Thoracic Spine Syndrome
Identifying the root causes of thoracic spine syndrome is essential for developing a targeted treatment plan. Several factors contribute to this syndrome, including:
- Poor Posture: Prolonged periods of poor posture, especially during desk work, can develop strain on the thoracic spine.
- Injury: Accidents or sports injuries can lead to sudden onset of symptoms related to thoracic spine syndrome.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: As we age, the discs in our spine naturally degenerate, which can lead to soreness and discomfort.
- Osteoarthritis: Wear and tear of the cartilage can cause pain in the thoracic spine and is common in older adults.
Key Symptoms of Thoracic Spine Syndrome
Individuals suffering from thoracic spine syndrome may experience a variety of symptoms. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to prompt treatment and relief:
- Localized Pain: Pain can be felt directly in the thoracic spine region, often exacerbated by certain movements.
- Radiating Pain: Pain may radiate to the shoulders, arms, and neck, mimicking other conditions.
- Numbness and Tingling: A pinched nerve can cause sensations of numbness or tingling in the upper body.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness in arm or shoulder muscles can occur as a result of nerve compression.
Diagnosis of Thoracic Spine Syndrome
Diagnosis plays a critical role in effectively treating thoracic spine syndrome. Health professionals use a combination of patient history, physical examinations, and diagnostic imaging to arrive at a definitive diagnosis:
1. Medical History
The first step involves gathering a comprehensive medical history to understand the onset and nature of the symptoms.
2. Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination will assess mobility, reflexes, and areas of tenderness in the thoracic spine region.
3. Imaging Studies
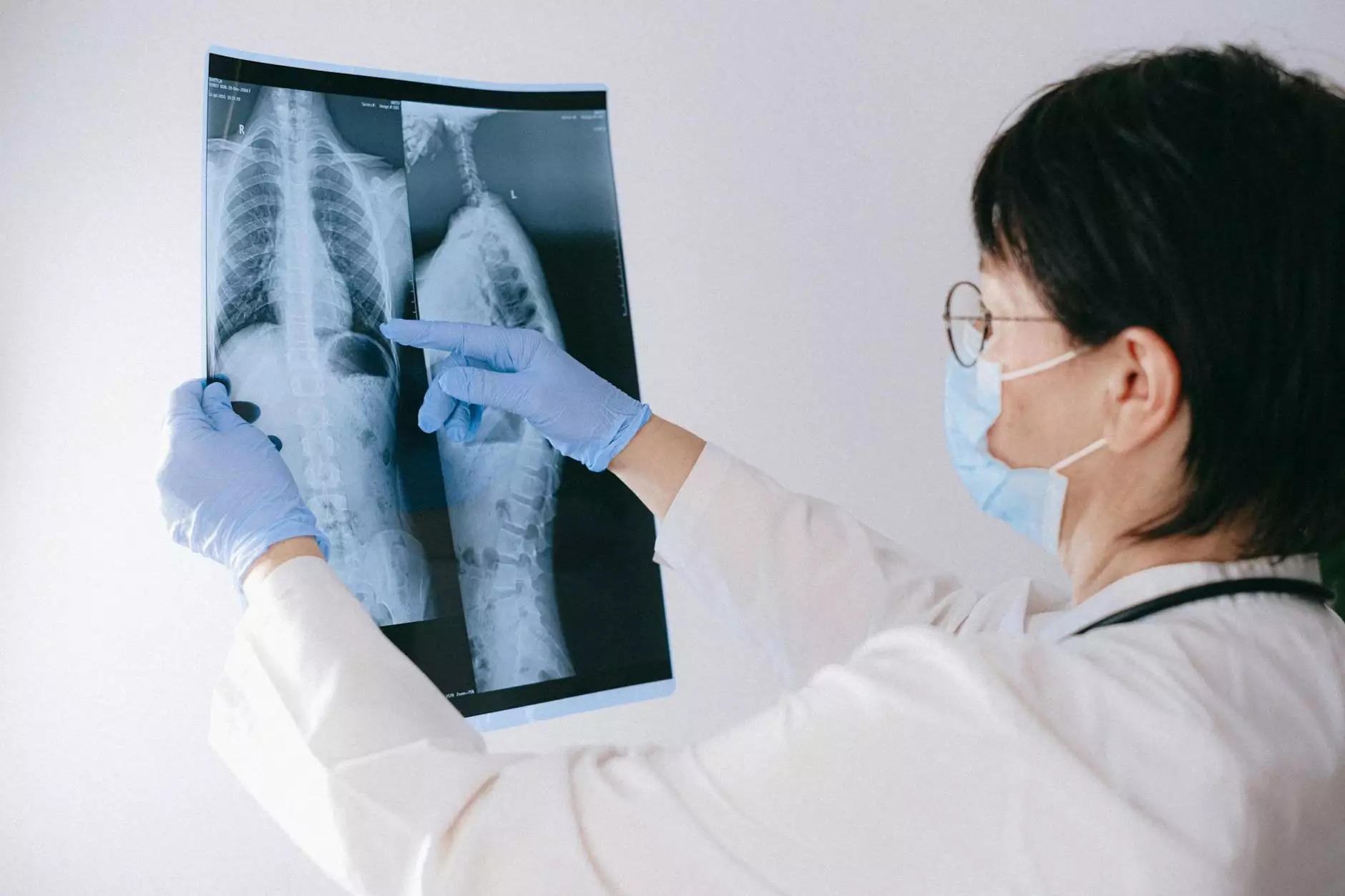
Diagnostic imaging such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans may be recommended to visualize the structures of the thoracic spine.
Treatment Options for Thoracic Spine Syndrome
Treating thoracic spine syndrome often requires a multifaceted approach tailored to the individual's symptoms and underlying causes. Here are some commonly recommended treatment options:
1. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is often the cornerstone of treatment for thoracic spine syndrome. A physical therapist can design a personalized rehabilitation program focusing on:
- Strengthening muscles supporting the spine.
- Improving flexibility and range of motion.
- Postural training to prevent further injury.
2. Chiropractic Care
Chiropractors use manual adjustment techniques to improve spinal function and alleviate pain associated with thoracic spine syndrome. Regular chiropractic adjustments can realign the spine, restore mobility, and reduce nerve irritation.
3. Pain Management
Pain management strategies may include:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., NSAIDs).
- Muscle relaxants prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Injections (e.g., corticosteroid injections) for severe pain relief.
4. Surgery
In cases where conservative treatments fail to relieve severe or persistent pain, surgical options may be considered. Surgical interventions may include:
- Discectomy to remove herniated disc material.
- Laminectomy to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
Preventing Thoracic Spine Syndrome
Prevention is always the best medicine. Here are several strategies to reduce the risk of developing thoracic spine syndrome:
- Maintain Correct Posture: Pay attention to your alignment during daily activities. Use chairs and cushions that support your back.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity strengthens the muscles surrounding the spine and improves flexibility.
- Use Ergonomic Workstations: Invest in ergonomic furniture and equipment to maintain a comfortable working environment.
Conclusion
Thoracic spine syndrome can severely impact an individual’s day-to-day life. Understanding this condition allows patients and health professionals to take proactive measures for effective management and treatment. Whether through physical therapy, chiropractic care, or a well-rounded approach to rehabilitation, it is crucial to address this complex syndrome promptly. By implementing preventative strategies and recognizing the symptoms early, individuals can enhance their quality of life significantly.
For more information on thoracic spine syndrome and effective treatment options, consult your healthcare provider or visit iaom-us.com.









